3.11
GPRS data transmission in the GSM network
To be able to use the original GSM network, which is exclusively circuit-oriented, packet-oriented transmission is introduced, it was necessary to supplement the original net structure with equipment as shown in the following figure. This new data transmission system is called GPRS.
+
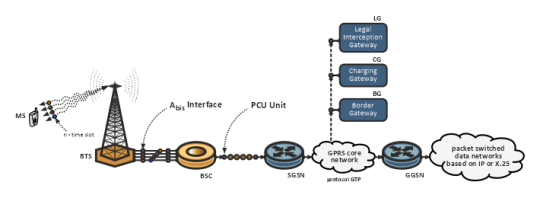
Fig. 19 Data transfer via GPRS.
Note
Data node SGSN communicates with the radio part of the GPRS network. To transmit data to other packet networks, such as the Internet, the GGSN data gateway is used, which acts as a router. APN (Access Point Name) is used to give the user access to defined networks. In this way, the operator can reserve access to a given APN only to a defined set of SIM cards and thus create a private group of users in the GPRS network, whose traffic is strictly separated from other traffic. It follows from the above that it is possible to create both public and private data networks in this way, and it is also possible to tariff individual operator services in different ways according to APN, such as WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) or MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service).
Note
Internet access is possible thanks to WAP technology, which makes the content of web servers and their information services available on mobile terminals even using low capacity channels and displays with a limited display range. The application of data communication and WAP is enabled in the entire range of GPRS technology with packet-oriented transmission and extended transmission speed theoretically up to 192 kbps. However, the introduction of this service required much more extensive and costly interventions not only in the structure of the GSM network but also in mobile devices.
Interesting
Advantage
Increasing the transmission speed of GPRS technology is possible by combining multiple channels for one subscriber in the radio part of the network and choosing a suitable coding system for this channel. In this context, we speak of transmission using 3+1, 4+1, or 4+2 channels (towards the subscriber + away from the participant). In the case of GPRS technology, asymmetric data transmission is used, where the direction to the subscriber is the preferred direction, i.e. it achieves a higher transmission speed.
Interesting
The values of the available transmission speed are strongly dependent on the specific location and its current load.
Disadvantage
In a GSM network with implemented GPRS, the negative effect of data packet delay caused by the passage of packets through the network is obvious. The value of the delay is strongly dependent on the size of the packets. Short packets (up to 100 bytes) have a transmission delay of 0.5 to 1 second, depending on the state and load of the network. On the other hand, packets with a size of up to 1 kB can have a delay of several seconds.